
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 018
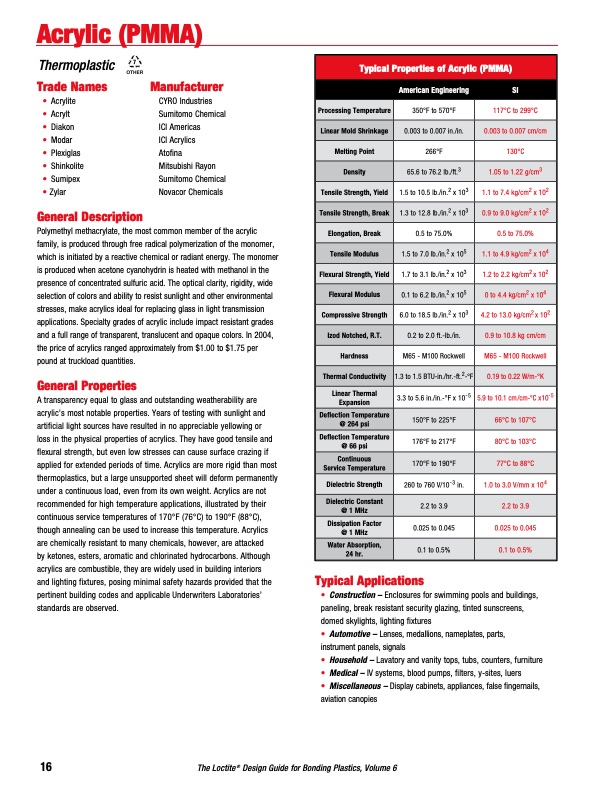
Acrylic (PMMA) Typical Properties of Acrylic (PMMA) American Engineering SI Processing Temperature 350°F to 570°F 117°C to 299°C Linear Mold Shrinkage 0.003 to 0.007 in./in. 0.003 to 0.007 cm/cm Melting Point 266°F 130°C Density 65.6 to 76.2 lb./ft.3 1.05 to 1.22 g/cm3 Tensile Strength, Yield 1.5 to 10.5 lb./in.2 x 103 1.1 to 7.4 kg/cm2 x 102 Tensile Strength, Break 1.3 to 12.8 lb./in.2 x 103 0.9 to 9.0 kg/cm2 x 102 Elongation, Break 0.5 to 75.0% 0.5 to 75.0% Tensile Modulus 1.5 to 7.0 lb./in.2 x 105 1.1 to 4.9 kg/cm2 x 104 Flexural Strength, Yield 1.7 to 3.1 lb./in.2 x 103 1.2 to 2.2 kg/cm2 x 102 Flexural Modulus 0.1 to 6.2 lb./in.2 x 105 0 to 4.4 kg/cm2 x 104 Compressive Strength 6.0 to 18.5 lb./in.2 x 103 4.2 to 13.0 kg/cm2 x 102 Izod Notched, R.T. 0.2 to 2.0 ft.-lb./in. 0.9 to 10.8 kg cm/cm Hardness M65 - M100 Rockwell M65 - M100 Rockwell Thermal Conductivity 1.3 to 1.5 BTU-in./hr.-ft.2-°F 0.19 to 0.22 W/m-°K Linear Thermal Expansion 3.3 to 5.6 in./in.-°F x 10-5 5.9 to 10.1 cm/cm-°C x10-5 Deflection Temperature @ 264 psi 150°F to 225°F 66°C to 107°C Deflection Temperature @ 66 psi 176°F to 217°F 80°C to 103°C Continuous Service Temperature 170°F to 190°F 77°C to 88°C Dielectric Strength 260 to 760 V/10-3 in. 1.0 to 3.0 V/mm x 104 Dielectric Constant @ 1 MHz 2.2 to 3.9 2.2 to 3.9 Dissipation Factor @ 1 MHz 0.025 to 0.045 0.025 to 0.045 Water Absorption, 24 hr. 0.1 to 0.5% 0.1 to 0.5% Thermoplastic Trade Names • Acrylite • Acrylt • Diakon • Modar • Plexiglas • Shinkolite • Sumipex • Zylar General Description Manufacturer CYRO Industries Sumitomo Chemical ICI Americas ICI Acrylics Atofina Mitsubishi Rayon Sumitomo Chemical Novacor Chemicals Polymethyl methacrylate, the most common member of the acrylic family, is produced through free radical polymerization of the monomer, which is initiated by a reactive chemical or radiant energy. The monomer is produced when acetone cyanohydrin is heated with methanol in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. The optical clarity, rigidity, wide selection of colors and ability to resist sunlight and other environmental stresses, make acrylics ideal for replacing glass in light transmission applications. Specialty grades of acrylic include impact resistant grades and a full range of transparent, translucent and opaque colors. In 2004, the price of acrylics ranged approximately from $1.00 to $1.75 per pound at truckload quantities. General Properties A transparency equal to glass and outstanding weatherability are acrylic’s most notable properties. Years of testing with sunlight and artificial light sources have resulted in no appreciable yellowing or loss in the physical properties of acrylics. They have good tensile and flexural strength, but even low stresses can cause surface crazing if applied for extended periods of time. Acrylics are more rigid than most thermoplastics, but a large unsupported sheet will deform permanently under a continuous load, even from its own weight. Acrylics are not recommended for high temperature applications, illustrated by their continuous service temperatures of 170°F (76°C) to 190°F (88°C), though annealing can be used to increase this temperature. Acrylics are chemically resistant to many chemicals, however, are attacked by ketones, esters, aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons. Although acrylics are combustible, they are widely used in building interiors and lighting fixtures, posing minimal safety hazards provided that the pertinent building codes and applicable Underwriters Laboratories’ standards are observed. Typical Applications • Construction – Enclosures for swimming pools and buildings, paneling, break resistant security glazing, tinted sunscreens, domed skylights, lighting fixtures • Automotive – Lenses, medallions, nameplates, parts, instrument panels, signals • Household – Lavatory and vanity tops, tubs, counters, furniture • Medical – IV systems, blood pumps, filters, y-sites, luers • Miscellaneous – Display cabinets, appliances, false fingernails, aviation canopies 16 The Loctite® Design Guide for Bonding Plastics, Volume 6PDF Image | Design Guide for Bonding Plastics Volume 6 LT-2197
PDF Search Title:
Design Guide for Bonding Plastics Volume 6 LT-2197Original File Name Searched:
henkel-loctite-design-guide-plastic-bonding.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Development of a solar powered Electric Ship The Electricship website originally started off as a project to develop a comprehensive renewable, affordable, modular electric ship... More Info
Modular Boat Hull Composite The case for a unsinkable, modular composite hybrid boat hull... More Info
MS Burgenstock Hybrid Electric Catamaran Lake Lucerne Unique shuttle servicing Lucerne to the Burgenstock Resort... More Info
Ground Power Unit GPU Powered by Lithium Ion Batteries The goal of the Ground Power Unit is to provide a readily accessible, modular, ready-to-power solution for remote power... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@electricship.com | RSS | AMP |