
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 030
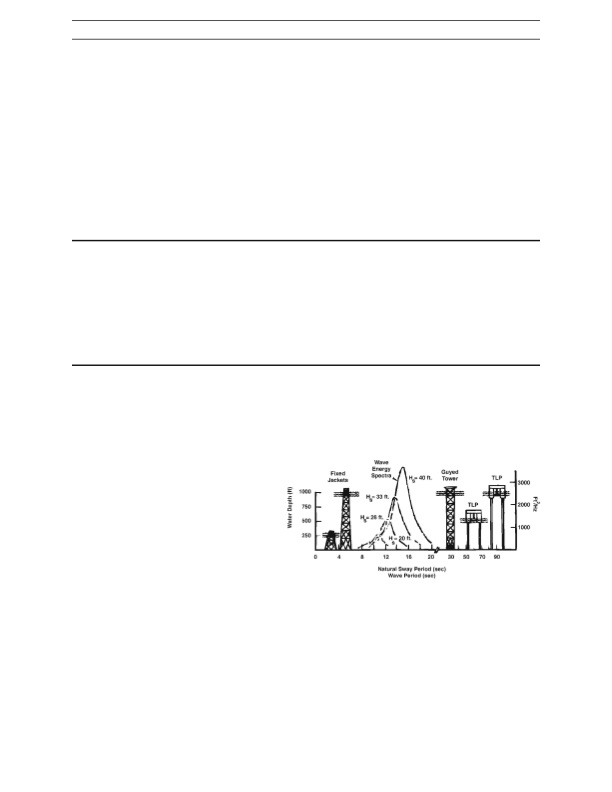
Chapter One APPLICATIONS Slingsby Engineering Limited designed and developed a third-generation remotely operated vehicle calledSolo for a variety of inspection and maintenance functions in the offshore industry. Solo carries a comprehensive array of sophisticated equipment and is designed to operate at a depth of 5,000 feet under a hydrostatic pressure of 2 ksi. The pressure hull, chassis and fairings are constructed of glass fiber woven roving. [1-13] A prototype civilian submarine has been built in Italy for offshore work. The design consists of an unpressurized, aramid-epoxy outer hull that offers a better combination of low weight with improved stiffness and impact toughness. The operational range at 12 knots has been extended by two hours over the range of a glass hull. [1-14] Navigational Aids Steel buoys in the North Sea are being progressively replaced with plastic buoys due to increasing concern of damage to vessels. Balmoral Glassfibre produces a complete line of buoys and a light tower made of GRP that can withstand winds to 125 mph. Anchor mooring buoys supplied to the Egyptian offshore oil industry are believed to be the largest GRP buoys ever produced. These 13 foot diameter, 16.5 ton reserve buoyancy moorings are used to anchor tankers of up to 330,600 ton capacity. [1-15] Offshore Engineering At a September, 1990 conference sponsored by the Ship Structure Committee and the National Academy of Sciences entitledTh�e Use of Composite Materials in Load-Bearing Marine Structures,� Jerry Williams of Conoco reported that composites show the potential for improved corrosion resistance and weight reduction for numerous applications in offshore oil recovery structures. The Tension Leg Platform (TLP) is a leading candidate for oil and gas production facilities in deep water. Figure 1-15 shows how these structures react to wave energy versus fixed-leg platforms. TLP’s are extremely weight sensitive and could benefit from composite tendons and floating structure. Williams also proposes the use of pultruded composite piping similar to the configurations shown in Figure 1-16. The piping needs to resist 1000 psi internal loads, have good longitudinal strength and stiffness (see 0� Figure 1-15 ships. [1-16] liams, Conoco] Composite materials are already being used in offshore hydrocarbon production because of their weight, resistance to corrosion and good mechanical properties. One proposed new use for composites is for submarine pipelines, with circumferential carbon fibers providing resistance to external pressure and longitudinal glass fibers providing lengthwise flexibility. [1-9] graphite), and must be able to roll on a large spool for use with cable laying od Relative to Sea State Energy [Jerry Wil- 17 Platform Natural Sway Peri-PDF Image | Marine Componsites
PDF Search Title:
Marine ComponsitesOriginal File Name Searched:
MARINE_COMPOSITES.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Development of a solar powered Electric Ship The Electricship website originally started off as a project to develop a comprehensive renewable, affordable, modular electric ship... More Info
Modular Boat Hull Composite The case for a unsinkable, modular composite hybrid boat hull... More Info
MS Burgenstock Hybrid Electric Catamaran Lake Lucerne Unique shuttle servicing Lucerne to the Burgenstock Resort... More Info
Ground Power Unit GPU Powered by Lithium Ion Batteries The goal of the Ground Power Unit is to provide a readily accessible, modular, ready-to-power solution for remote power... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@electricship.com | RSS | AMP |