
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 013
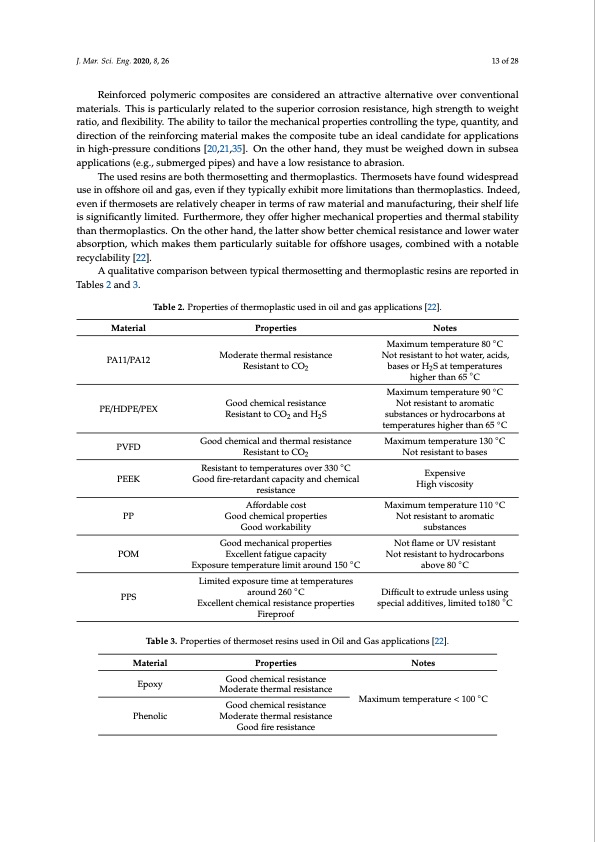
J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 26 13 of 28 Reinforced polymeric composites are considered an attractive alternative over conventional materials. This is particularly related to the superior corrosion resistance, high strength to weight ratio, and flexibility. The ability to tailor the mechanical properties controlling the type, quantity, and direction of the reinforcing material makes the composite tube an ideal candidate for applications in high-pressure conditions [20,21,35]. On the other hand, they must be weighed down in subsea applications (e.g., submerged pipes) and have a low resistance to abrasion. The used resins are both thermosetting and thermoplastics. Thermosets have found widespread use in offshore oil and gas, even if they typically exhibit more limitations than thermoplastics. Indeed, even if thermosets are relatively cheaper in terms of raw material and manufacturing, their shelf life is significantly limited. Furthermore, they offer higher mechanical properties and thermal stability than thermoplastics. On the other hand, the latter show better chemical resistance and lower water absorption, which makes them particularly suitable for offshore usages, combined with a notable recyclability [22]. A qualitative comparison between typical thermosetting and thermoplastic resins are reported in Tables 2 and 3. Material PA11/PA12 PE/HDPE/PEX PVFD PEEK PP POM PPS Properties Moderate thermal resistance Resistant to CO2 Good chemical resistance Resistant to CO2 and H2S Good chemical and thermal resistance Resistant to CO2 Resistant to temperatures over 330 ◦C Good fire-retardant capacity and chemical resistance Affordable cost Good chemical properties Good workability Good mechanical properties Excellent fatigue capacity Exposure temperature limit around 150 ◦C Limited exposure time at temperatures around 260 ◦C Excellent chemical resistance properties Fireproof Notes Maximum temperature 80 ◦C Not resistant to hot water, acids, bases or H2S at temperatures higher than 65 ◦C Maximum temperature 90 ◦C Not resistant to aromatic substances or hydrocarbons at temperatures higher than 65 ◦C Maximum temperature 130 ◦C Not resistant to bases Expensive High viscosity Maximum temperature 110 ◦C Not resistant to aromatic substances Not flame or UV resistant Not resistant to hydrocarbons above 80 ◦C Difficult to extrude unless using special additives, limited to180 ◦C Table 2. Properties of thermoplastic used in oil and gas applications [22]. Table 3. Properties of thermoset resins used in Oil and Gas applications [22]. Material Epoxy Phenolic Properties Good chemical resistance Moderate thermal resistance Good chemical resistance Moderate thermal resistance Good fire resistance Notes Maximum temperature < 100 ◦CPDF Image | Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced Composites
PDF Search Title:
Marine Application of Fiber Reinforced CompositesOriginal File Name Searched:
jmse-08-00026.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Development of a solar powered Electric Ship The Electricship website originally started off as a project to develop a comprehensive renewable, affordable, modular electric ship... More Info
Modular Boat Hull Composite The case for a unsinkable, modular composite hybrid boat hull... More Info
MS Burgenstock Hybrid Electric Catamaran Lake Lucerne Unique shuttle servicing Lucerne to the Burgenstock Resort... More Info
Ground Power Unit GPU Powered by Lithium Ion Batteries The goal of the Ground Power Unit is to provide a readily accessible, modular, ready-to-power solution for remote power... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@electricship.com | RSS | AMP |