
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 017
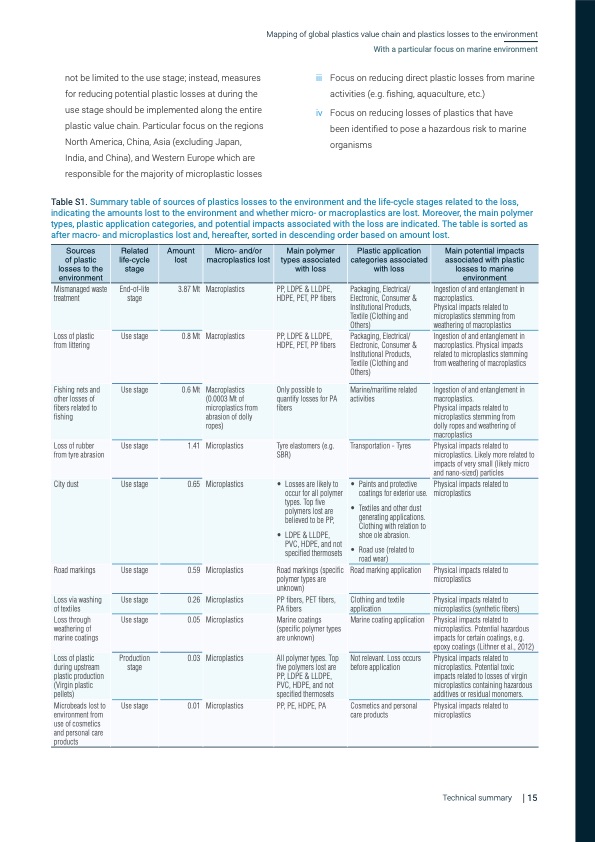
not be limited to the use stage; instead, measures for reducing potential plastic losses at during the use stage should be implemented along the entire plastic value chain. Particular focus on the regions North America, China, Asia (excluding Japan, India, and China), and Western Europe which are responsible for the majority of microplastic losses Mapping of global plastics value chain and plastics losses to the environment With a particular focus on marine environment iii Focus on reducing direct plastic losses from marine activities (e.g. fishing, aquaculture, etc.) iv Focus on reducing losses of plastics that have been identified to pose a hazardous risk to marine organisms Table S1. Summary table of sources of plastics losses to the environment and the life-cycle stages related to the loss, indicating the amounts lost to the environment and whether micro- or macroplastics are lost. Moreover, the main polymer types, plastic application categories, and potential impacts associated with the loss are indicated. The table is sorted as after macro- and microplastics lost and, hereafter, sorted in descending order based on amount lost. Sources of plastic losses to the environment Related life-cycle stage Amount lost Micro- and/or macroplastics lost Main polymer types associated with loss Plastic application categories associated with loss Main potential impacts associated with plastic losses to marine environment Mismanaged waste treatment End-of-life stage 3.87 Mt Macroplastics PP, LDPE & LLDPE, HDPE, PET, PP fibers Packaging, Electrical/ Electronic, Consumer & Institutional Products, Textile (Clothing and Others) Ingestion of and entanglement in macroplastics. Physical impacts related to microplastics stemming from weathering of macroplastics Loss of plastic from littering Use stage 0.8 Mt Macroplastics PP, LDPE & LLDPE, HDPE, PET, PP fibers Packaging, Electrical/ Electronic, Consumer & Institutional Products, Textile (Clothing and Others) Ingestion of and entanglement in macroplastics. Physical impacts related to microplastics stemming from weathering of macroplastics Fishing nets and other losses of fibers related to fishing Use stage 0.6 Mt Macroplastics (0.0003 Mt of microplastics from abrasion of dolly ropes) Only possible to quantify losses for PA fibers Marine/maritime related activities Ingestion of and entanglement in macroplastics. Physical impacts related to microplastics stemming from dolly ropes and weathering of macroplastics Loss of rubber from tyre abrasion Use stage 1.41 Microplastics Tyre elastomers (e.g. SBR) Transportation - Tyres Physical impacts related to microplastics. Likely more related to impacts of very small (likely micro and nano-sized) particles City dust Use stage 0.65 Microplastics • Losses are likely to occur for all polymer types. Top five polymers lost are believed to be PP, • LDPE & LLDPE, PVC, HDPE, and not specified thermosets • Paints and protective coatings for exterior use. • Textiles and other dust generating applications. Clothing with relation to shoe ole abrasion. • Road use (related to road wear) Physical impacts related to microplastics Road markings Use stage 0.59 Microplastics Road markings (specific polymer types are unknown) Road marking application Physical impacts related to microplastics Loss via washing of textiles Use stage 0.26 Microplastics PP fibers, PET fibers, PA fibers Clothing and textile application Physical impacts related to microplastics (synthetic fibers) Loss through weathering of marine coatings Use stage 0.05 Microplastics Marine coatings (specific polymer types are unknown) Marine coating application Physical impacts related to microplastics. Potential hazardous impacts for certain coatings, e.g. epoxy coatings (Lithner et al., 2012) Loss of plastic during upstream plastic production (Virgin plastic pellets) Production stage 0.03 Microplastics All polymer types. Top five polymers lost are PP, LDPE & LLDPE, PVC, HDPE, and not specified thermosets Not relevant. Loss occurs before application Physical impacts related to microplastics. Potential toxic impacts related to losses of virgin microplastics containing hazardous additives or residual monomers. Microbeads lost to environment from use of cosmetics and personal care products Use stage 0.01 Microplastics PP, PE, HDPE, PA Cosmetics and personal care products Physical impacts related to microplastics Technical summary | 15PDF Image | Mapping of global plastics value chain
PDF Search Title:
Mapping of global plastics value chainOriginal File Name Searched:
2018-plastics-global-hotspots.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Development of a solar powered Electric Ship The Electricship website originally started off as a project to develop a comprehensive renewable, affordable, modular electric ship... More Info
Modular Boat Hull Composite The case for a unsinkable, modular composite hybrid boat hull... More Info
MS Burgenstock Hybrid Electric Catamaran Lake Lucerne Unique shuttle servicing Lucerne to the Burgenstock Resort... More Info
Ground Power Unit GPU Powered by Lithium Ion Batteries The goal of the Ground Power Unit is to provide a readily accessible, modular, ready-to-power solution for remote power... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@electricship.com | RSS | AMP |